Hive(九)Hive数据压缩和hive查询优化
hive 压缩和优化
压缩
hadoop 执行阶段可以配置一些数据压缩策略以减少数据的传输。
</archives/39578da0.html#hadoop-%E6%95%B0%E6%8D%AE%E5%8E%8B%E7%BC%A9>
在hive执行的时候也可以指定启用压缩和压缩的相关的配置
开启数据压缩
1 | set hive.exec.compress.intermediate=true; |
hive 传输中的数据压缩开启
1 | set mapreduce.map.output.compress=true; |
map 阶段的输出的数据压缩开启
1 | set mapreduce.map.output.compress.codec= |
指定map阶段的数据压缩的实现方式
1 | set hive.exec.compress.output=true; |
hive 最终输出的数据的压缩开启
1 | set mapreduce.output.fileoutputformat.compress=true; |
开启mr 程序的输出的数据压缩
1 | set mapreduce.output.fileoutputformat.compress.codec = |
设置输出压缩的方式
1 | set mapreduce.output.fileoutputformat.compress.type=BLOCK; |
设置最终压缩类型为块压缩
存储格式
hive 支持多种存储格式 比如 TEXTFILE 、SEQUENCEFILE、ORC、PARQUET。
在数据存储的时候根据存储的方式不同,还可分为行存储和列存储。
假设 数据内容为
1 | 1 小明 |
如果是行存储,那么在文件中的排列方式将是
1 | 1 小明 2 小红 3 小绿 4 小黑 |
行存储的时候,获取一行的数据比较容易,因为一行的数据都是相邻的。
同理,列存储,就是一列的数据进行挨着存储
1 | 1 2 3 4 小明 小红 小绿 小黑 |
这种存储方式,在只查询对应的列信息的时候比较容易。
那么对于hive的存储格式中,
TEXTFILE和SEQUENCEFILE 是基于行存储。
ORC和PARQUET是列存储。
指定使用那种存储格式,可以在创建表的时候使用 stored as ocr 或 stored as parquet 即可
TEXTFILE
最简单的数据格式,默认格式,数据不压缩,数据解析的开销大。
OCR
ocr文件的wiki连接 https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/Hive/LanguageManual+ORC
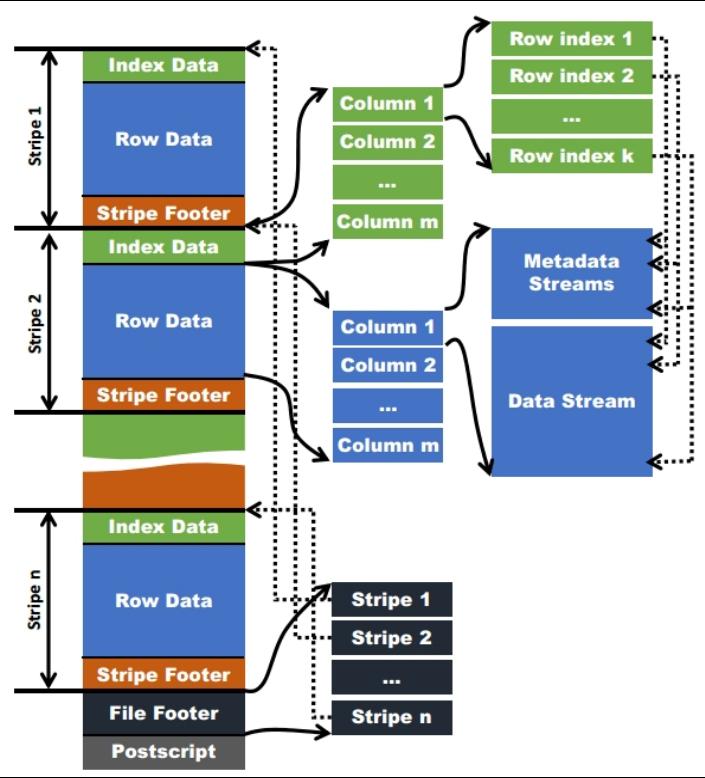
OCR 的文件结构
每个文件由多个stripe 组成。一个stripe 一般为一个hdfs的一个块大小(默认128M);针对这些行的数据做一个列的存储。
一个stripe 由三部分组成 IndexData,RowData,Stripe Footer。
IndexData 索引数据 存了记录某行的各字段在Row Data中的offset。
Row Data 是具体的数据。
Stripe Footer:存的是各个Stream的类型,长度等信息。
https://blog.csdn.net/maizi1045/article/details/79667857
Parquet
wiki链接 https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/Hive/Parquet
Parquet文件是以二进制方式存储的,所以是不可以直接读取的,文件中包括该文件的数据和元数据,因此Parquet格式文件是自解析的。
- 行组(Row Group):每一个行组包含一定的行数,在一个HDFS文件中至少存储一个行组,类似于orc的stripe的概念。
- 列块(Column Chunk):在一个行组中每一列保存在一个列块中,行组中的所有列连续的存储在这个行组文件中。一个列块中的值都是相同类型的,不同的列块可能使用不同的算法进行压缩。
- 页(Page):每一个列块划分为多个页,一个页是最小的编码的单位,在同一个列块的不同页可能使用不同的编码方式。
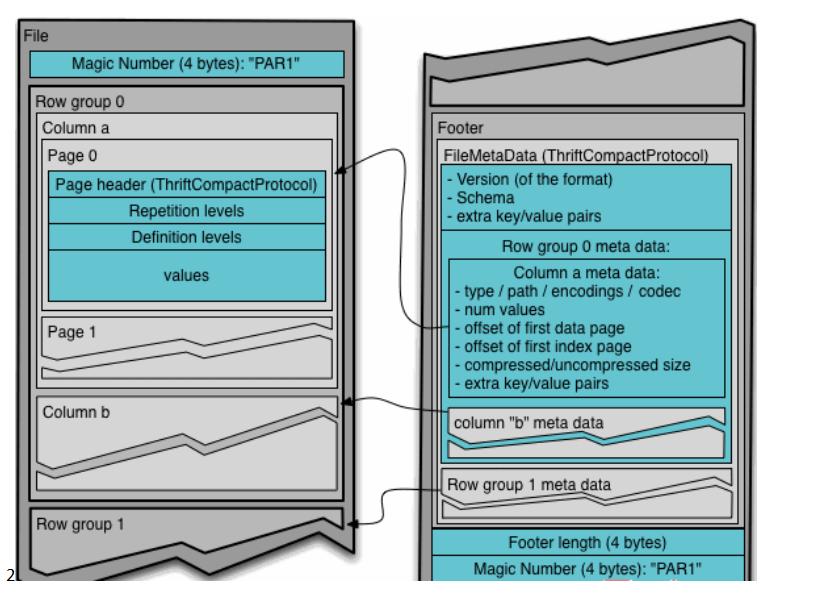
https://blog.csdn.net/javastart/article/details/124528452
使用存储和压缩处理文件输出格式
创建一个表使用ocr的输出格式
ocr 是用的比较多的一种输出格式
在创建表的tblproperties 信息中,可以添加一些ocr的相关参数信息。

创建表使用 ocr 格式和zlib压缩
1 | create table info(id int ,name string) |

优化
查询执行计划
使用explain 可以类似于mysql 那样看到具体的执行计划信息。
EXPLAIN [EXTENDED | DEPENDENCY | AUTHORIZATION] query
为了能够得到更好的执行效率和执行效果,需要先通过explain 看下执行计划。此执行计划是hive已经优化了的计划。
对于hive的执行分为2种 ,一种走MR 程序的,一种不走MR程序的,不走MR程序的执行性能远远大于走MR程序的,通过explain 可以看出具体的执行是否走了MR 和走了几个MR。
1 | explain select * from emp; |
一个检查的查询所有的数据的执行计划
1 |
|
可以看到执行计划总共只有一步。做了一个Fetch 操作,也就是数据的拉取,limit -1 表示拉取所有的数据.
1 | explain select job,count(job) from emp group by job; |
查看一个聚合操作的执行计划;
1 |
|
聚合操作是需要走MR程序的。
STAGE DEPENDENCIES 看到总共的执行步骤,目前是有2步。 Stage-1 和 Stage-0 ,其中 Stage-0 依赖于 Stage-1
Stage-1 的执行计划就是一个MR程序.
可以看到Map 程序中 keys 用的是job ,聚合操作是 aggregations count(job),并且map输出的结果是 _col10
看到reduce 程序中 的key 是 KEY._col0 aggregations 是 count(VALUE._col0)
Stage-0 的执行计划是hive中 hdfs中的一个数据的fetch操作。
在执行大数据量的操作的时候,通过explain 进行优化是必须的,能够减少执行时间。默认的MR程序如果执行时间超过7天,将被系统停止运行。
fetch 抓取配置
hive 是如何决定那些查询走fetch 操作还是走MR程序呢?
内部是有个参数来控制的,可以修改hive-site.xml 来进行设置.
参数名称 hive.fetch.task.conversion
有3个选项
- none 任何操作都会走mr程序
- minimal SELECT STAR, FILTER on partition columns, LIMIT only 只有这些操作会有fetch操作
- more SELECT, FILTER, LIMIT only (support TABLESAMPLE and virtual columns) 在minimal 的基础上,在全局 查找,字段查找,limit查找等都不走mapreduce.
测试:
- 查询当前的配置
1 | set hive.fetch.task.conversion; |
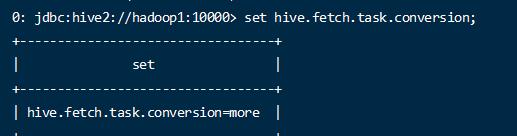
默认的配置是more,尽量的使用fetch操作
- 执行简单的查询过滤操作
1 | explain select ename,job from emp where job = 'CLERK'; |
可以看到执行这些操作的时候并没有走MR;
- 修改配置
1 | set hive.fetch.task.conversion=minimal; |
1 | explain select ename,job from emp where job = 'CLERK' and mgr > 10; |
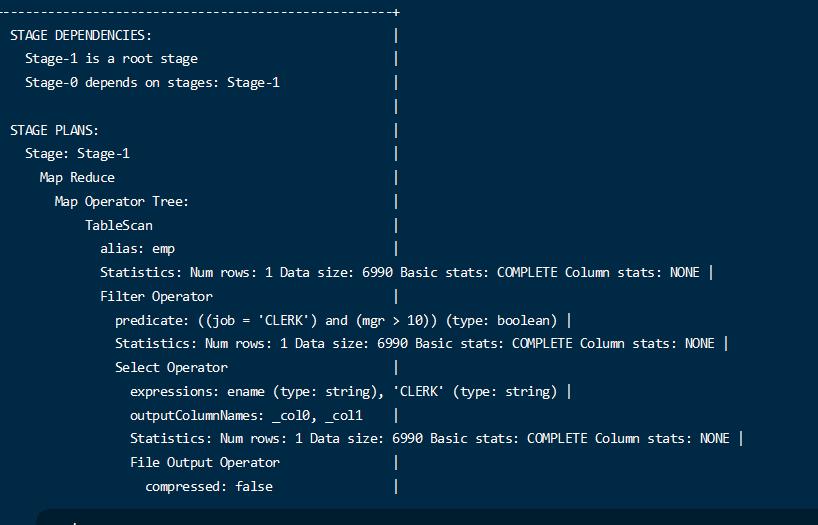
执行简单的过滤也走MR了
- 修改所有走mr
1 | set hive.fetch.task.conversion=none; |
可以发现任何查询都走MR了.
1 | explain select * from emp; |
本地模式配置
默认的hive 的查询提交到 MapReduce 通过集群 由yarn来调度任务。
这个过程会有一些性能的消耗,而对于有些小数据量的场景,可能开辟任务和调度的消耗 比处理任务的时候还长,这时候就是杀猪焉用宰牛刀。
可以配置本地运行默认,减少运行的消耗。
hive.exec.mode.local.auto=true 设置开启本地模式;
hive.exec.mode.local.auto.inputbytes.max=50000000 设置本地模式的最大数据量(50M 左右,本位byte)
hive.exec.mode.local.auto.input.files.max 本地模式的最大文件数量
下面2个配置是当开启了本地模式的时候,还得满足这2个条件才能使用本地模式
- 开始本地模式
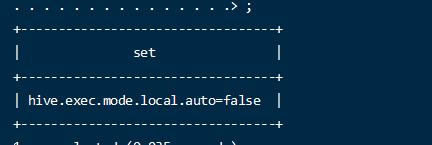
默认是关闭的
1 | set hive.exec.mode.local.auto=true; |
- 执行任务
1 | select deptno,avg(mgr) from emp group by deptno; |
结果出现错误

查看hive 日志看出是内存溢出
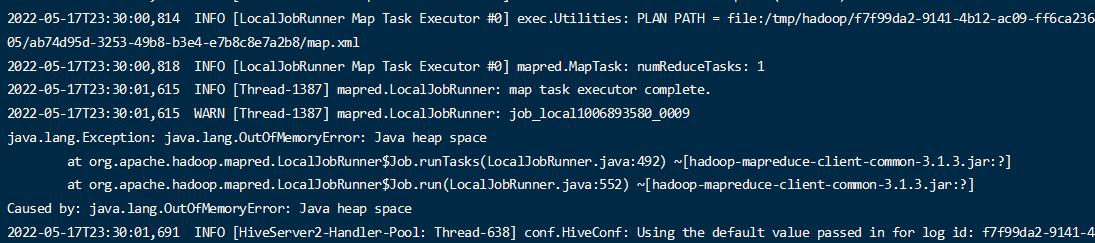
调整内存大小,重新执行
修改hive-env.sh
1 | //放开注释 |
重启hive
重新执行分区查询
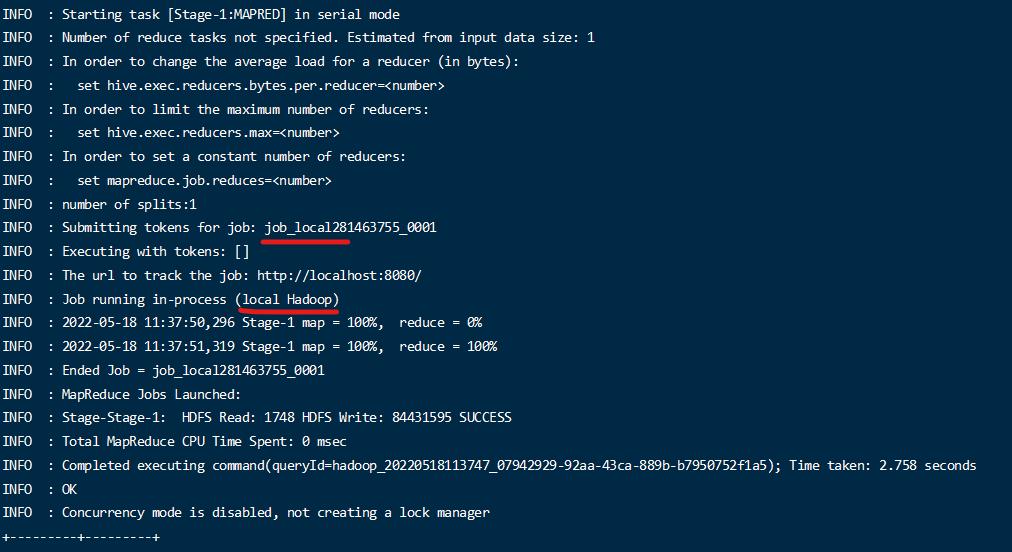
查看日志,可以看出目前已经是本地模式运行了;
- 小数据量下执行时间比较
比较本地模式的和集群模式的运行时间的区别,可以看出小数据量本地模式快于集群模式;
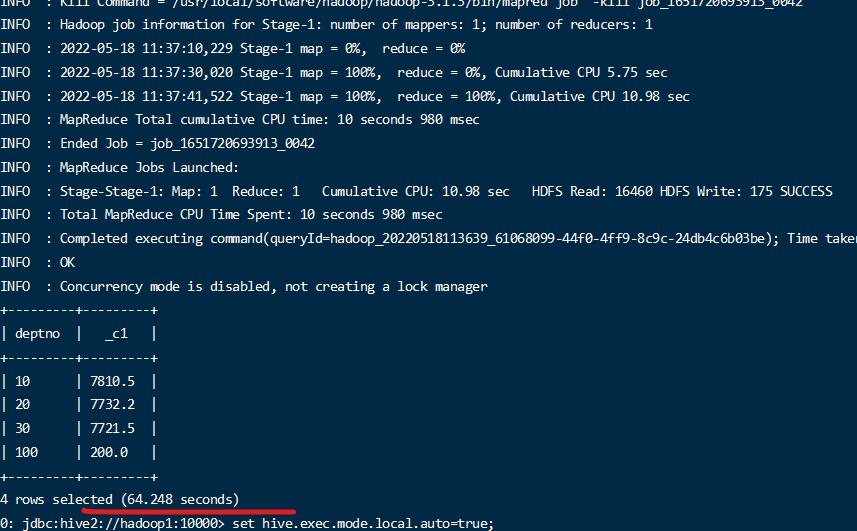
表查询优化
小表连接大表优化
表连接分为2种,一种是在Reduce 阶段连接,一种是把一个小表再Map阶段缓存起来,在Map阶段连接,称为MapJoin。
小表连接大表的场景非常适合MapJoin的方式。
并且在写sql的时候要使用小表来join大表。
新版 hive 已经优化小表join 大 和 大 join 小一个效果了。不过还是尽量用小的join 大的比较好。
开始mapjoin配置
hive.auto.convert.join = true 开启
hive.mapjoin.smalltable.filesize = 25000000 (25M) 小表的大小定义,只有小于这个值才是小表
注意:默认是开启的,默认值是25000000
- 开启
1 | set hive.auto.convert.join = true; |
查看执行计划
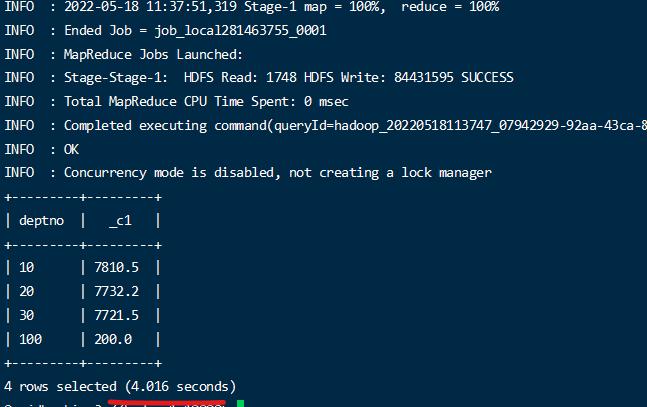
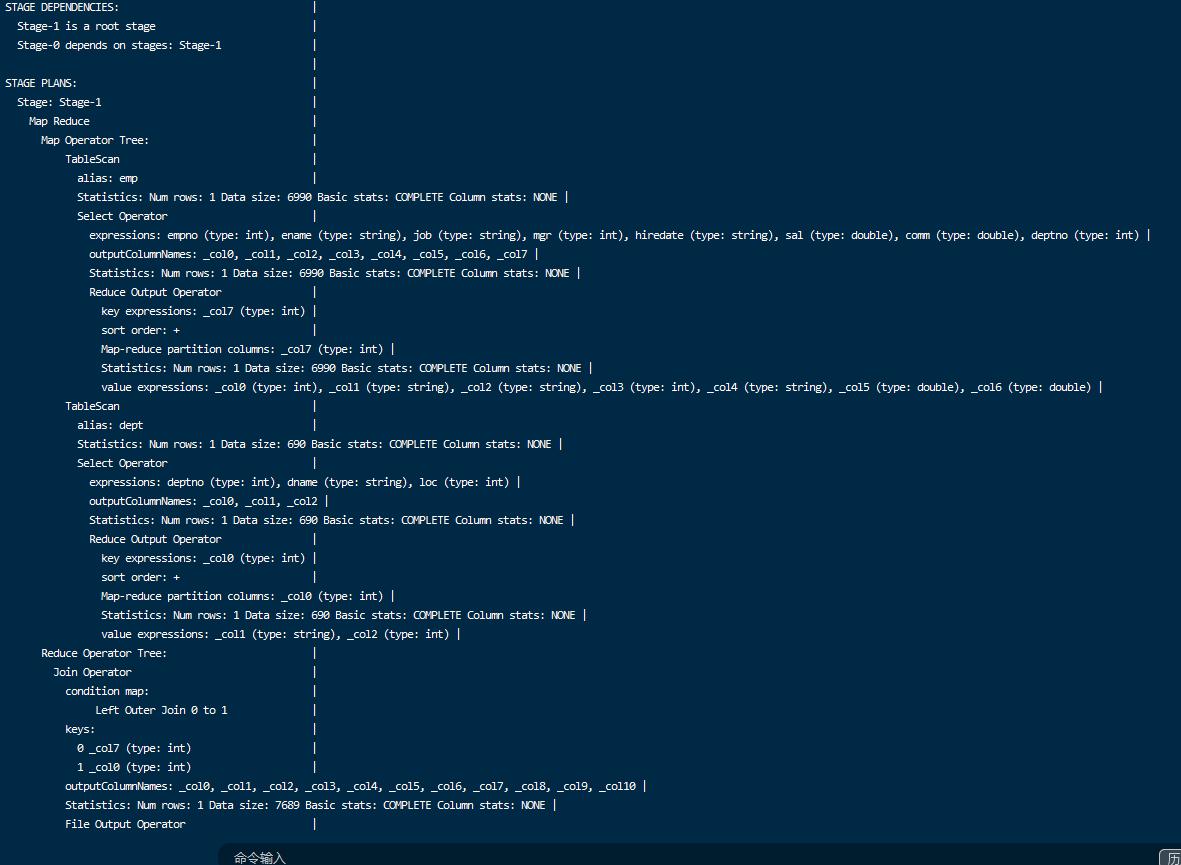
1 | explain select * from emp left join dept on emp.deptno = dept.deptno; |
通过执行计划,可以看到执行使用了mapjoin
- 查看关闭的执行计划
1 | set hive.auto.convert.join = false; |
查看执行计划
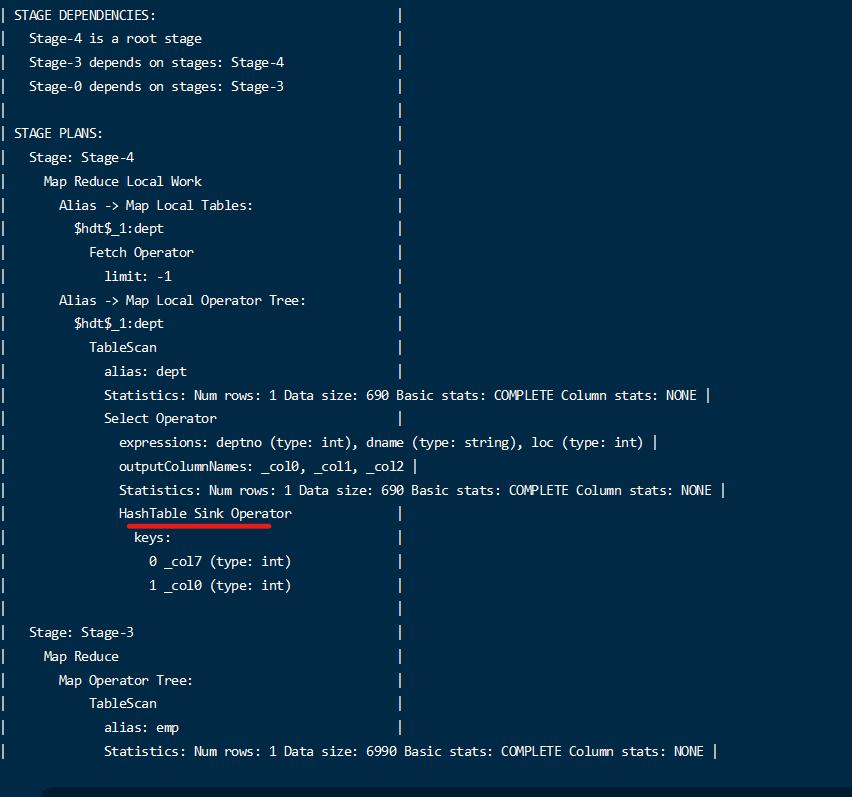
1 | explain select * from emp left join dept on emp.deptno = dept.deptno; |
可以看到并没有使用mapjoin
大表连接大表优化
null key 过滤
比如一个连接查询
1 | select * from emp left join dept on emp.deptno = dept.deptno; |
如果不希望emp 中的 deptno 为null的出现在结果中,那么先对数据进行过滤,减少关联操作的数据量,对关联的数据能够减少处理的范围。
1 |
|
空null转换
如果一个表中确实需要一些空值,但是又不能过滤,那么在执行的时候,这些空值就会由同一个maptask 来处理,空值很多的情况下,就会造成数据倾斜问题。
为了解决数据倾斜问题,把数据的空值处理成一个随机的值,让其能够分散到不同的maptask上。
- 测试数据准备一些有nullid的数据
1 | create table nullidtable(id bigint, t bigint, uid string, keyword string, url_rank int, click_num int, click_url string) row format delimited fields terminated by '\t'; |
加载数据
1 | load data local inpath '/home/hadoop/data/nullid' into table nullidtable; |
没有null 的表
1 | create table bigtable(id bigint, t bigint, uid string, keyword string, url_rank int, click_num int, click_url string) row format delimited fields terminated by '\t'; |
加载数据
1 | load data local inpath '/home/hadoop/data/bigtable' into table bigtable; |
两个文件的地址: https://www.aliyundrive.com/s/e62Xpw7WzD1 提取码: 3u9t
- 查看数据的个数
- 执行关联查询
//设置5个 reducejob 数量
1 | set mapreduce.job.reduces=5; |
1 | insert overwrite directory '/join/join1' select n.* from nullidtable n left join bigtable b on n.id = b.id; |
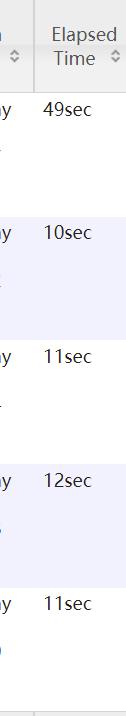
在reduce阶段有一些数据倾斜;
- 通过为null增加随机值。
1 | insert overwrite directory '/join/join2' select n.* from nullidtable n full join bigtable o on nvl(n.id,rand()) = o.id; |
使用nvl 将空值处理成随机数,注意随机数不能正好关联上错误的数据.
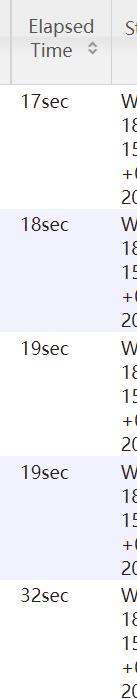
现在reduce 节点的执行将是比较均衡的。
SMB(Sort Merge Bucket join)
当数据量比较大的时候,为了达到连接查询的高效果,可以通过连接键进行分桶 的方式。
比如 数据表 A 和数据表 B ,数据量都是10w 。如果直接关联将是 10w 数据量去关联10
w数据,当分成4 个桶的时候, 每个表都根据桶的数量hash 分为了4个文件,并且只会两两关联,不会出现一个文件去其他的文件关联,达到一种拆分的目的。
开启参数:
1 | set hive.optimize.bucketmapjoin = true; |
默认关闭的
- 创建分桶表
分桶表1
1 | create table bigtable_buck1( |
1 | insert into bigtable_buck1 select * from bigtable; |
分桶表2
1 | create table bigtable_buck2( |
- 执行开启命令
1 | set hive.optimize.bucketmapjoin = true; |
- 测试关联时间
1 | insert overwrite directory '/join/join3' select b1.* from bigtable_buck1 b1 full join bigtable_buck2 b2 on b1.id = b2.id; |
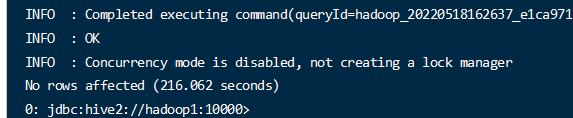
- 测试不使用分桶的表的关联时间
1 | create table bigtable_test_1( |
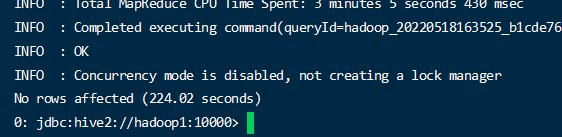
可以看到通过使用分桶的比不分桶的要快,当数据量大的时候结果对比才明显。
执行关联查询
1 | insert overwrite directory '/join/join6' select t1.* from bigtable_test_1 t1 full join bigtable_test_2 t2 on t1.id = t2.id; |
Group By 优化
主要针对有些聚合操作是可以在map阶段先完成一部分的。先在map阶段完成一部分,在reduce阶段得到最终的结果。
比如一个 分组后的 count 操作,原本是 map阶段分组,而reduce阶段计算 总数,而将计算总数的操作 让多个map先计算了,reduce来做个总和,可以防止数据倾斜,同时提高效率。
开启map端聚合
set hive.map.aggr = true 是否开启,(默认开启)
et hive.groupby.mapaggr.checkinterval = 100000 聚合操作的数量,每多少条数据执行一次聚合,最终reduce端将所有的结果合并。
set hive.groupby.skewindata = true 有数据倾斜的时候进行负载均衡
数据倾斜的数据进行负载开启后,生成的查询会有2个MR job。第一个MR Job中,Map的输出结果会随机分布到Reduce中,每个Reduce做部分聚合操作,并输出结果,这样处理的结果是相同的Group By Key有可能被分发到不同的Reduce中,从而达到负载均衡的目的;第二个MR Job再根据预处理的数据结果按照Group By Key分布到Reduce中(这个过程可以保证相同的Group By Key被分布到同一个Reduce中),最后完成最终的聚合操作。
- 开启测试
1 | set hive.map.aggr=true; |
1 | select deptno from emp group by deptno; |
- 关闭测试
1 | set hive.map.aggr=false; |
注意:当数据量小的时候可能看不出效果
COUNT(Distinct) 优化
默认的Distinct 使用reduce 来完成,当数据量大的时候,可能会很慢。
可以通过group by 的方式来完成,group by的方式还能用到map 端聚合。
1 | select count(id) from (select id from bigtable group by id) a; |
行列过滤
列过滤
列过滤就是查询的时候只查询特定的列减少数据的传输。
行过滤
在关联查询的时候,尽量将数据缩小到一个比较小的范围。
比如查询:
1 |
|
改写成:
1 |
|
通过下面的写法,可以在关联之前做到将行的数据过滤掉,减少mapreduce 的处理的数据范围;
注意:上面的那种写法,默认也会优化成下面的过滤,这种优化叫谓词下推。但是仅仅适用于简单的查询,复杂的查询无法自动优化,所以还是手动写成这样比较好。
设置map 和reduce 数量
针对map 和reduce 的数量设置,需要 根据多方面进行考虑。
主要的决定因素有:input的文件总个数,input的文件大小,集群设置的文件块大小。
如何调整map数量
- 每个map 数量处理的文件数尽量接近文件块(默认128m)的数量
- 针对比较耗时的文件,需要大量计算性能的文件,需要增加map数量,提高执行效率。
如何调reduce 数量
- 系统 自动方式
每个Reduce处理的数据量默认是256MB
参数1:set hive.exec.reducers.bytes.per.reducer=256000000
每个任务最大的reduce数,默认为1009
参数2:hive.exec.reducers.max=1009
N=min(参数2,总输入数据量/参数1)
- 设置方式 手动设置和修改
在hadoop的mapred-default.xml文件中修改
设置每个job的Reduce个数
set mapreduce.job.reduces = 15;
注意:reduce 数量等于生成的文件数,需要根据具体的业务场景选择具体的数量
小文件进行合并CombineHiveInputFormat
在hive中可以指定 hive的输入格式 CombineHiveInputFormat 来合并小文件。
在map执行前将小文件合并,减少了map数量。
map输入时的设置:
1 | //设置格式 |
map-reduce 任务结束时的设置:
1 |
|
是否合并map 阶段执行完毕的小文件 (默认开启)
1 | SET hive.merge.mapredfiles = true; |
是否合并reduce 阶段执行完毕的小文件 (默认关闭)
1 | SET hive.merge.size.per.task = 268435456; |
合并文件的最大大小,默认是 256000000
1 | SET hive.merge.smallfiles.avgsize = 16777216; 16M 左右 |
当小文件的平均大小,小于此值的时候,单独起一个mr任务执行合并任务。 此目的是因为文件太小,合并会耗费性能,加快合并。
并行模式
将map 阶段和reduce 阶段的多个任务之间,是可以并行执行的。
在map还未完全执行完的时候就启动了reduce,已经开始执行了部分的数据。
开启
1 | set hive.exec.parallel=true; //打开任务并行执行 |
默认是关闭的,在性能满足的情况下可以适当开启,减少程序处理时间。


