Spring Security(4)授权功能配置
授权
基本说明
授权指的是给用户某个操作的权限;
常见的权限的访问控制一般是 基于rpac (Role-Based Access Control)的 访问控制;
Authentication 是springsecurity 中的非常重要的接口;能够获取登录用户的信息和授权的相关信息;
而授权的信息是通过 Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities(); 此方法获取
GrantedAuthority 也只有一个返回Authority 的方法是一个字符串;
1 | public interface GrantedAuthority extends Serializable { |
这个字符串就是权限编码的信息;需要注意的是在springsecurity 中不管角色code 或权限code 都是从getAuthorities 方法获取。是不分区的,区分的标识只是看是否有 ROLE_ 这个前缀
比如 用户的授权信息是 [ “ROLE_USER”,”ROLE_ADMIN”, “user_edit”] 表示的是 具有USER 角色或ADMIN角色 权限和user_edit权限;
登录时查询权限信息
在自定义的 UserDetailService 查询用户信息的时候需要将授权信息也查询出来;
在之前章节的自定义的 MyUserDetails 是未处理授权的相关信息的,这里需要对授权信息的设置开发出来以便于设置权限和角色信息同时实现 getAuthorities 接口;
添加存储角色和权限的list
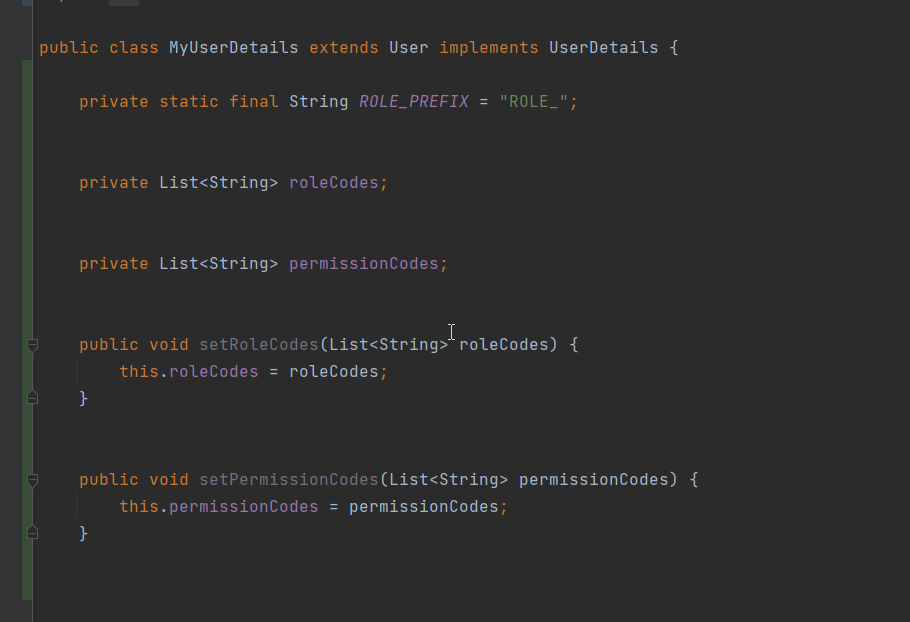
实现 getAuthorities 方法,注意角色的权限处理,需要加固定的前缀不然会当成普通的权限处理

在UserDetailsService 查询用户信息的时候设置权限信息
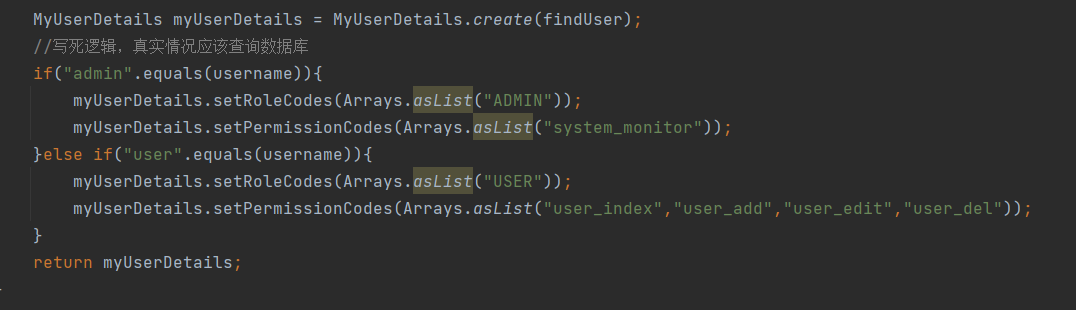
在这里给user 用户设置了user 角色和一些权限;
给admin 用户设置了admin角色和 一个权限;
当使用user用户登录后,通过打印授权信息,可以看到当前用户的授权code
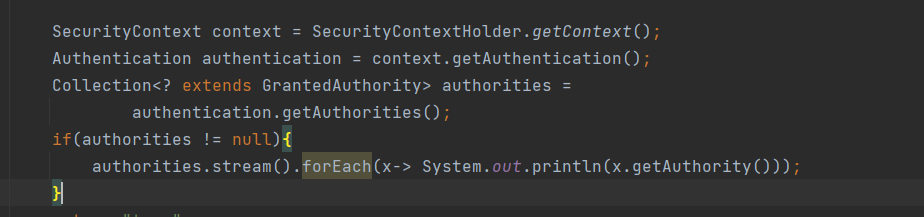

配置权限控制
配置认证权限通过配置 http.authorizeRequests() 来定义权限;
1 | http.authorizeRequests() |
配置说明:
- admin 开头的请求需要拥有 ROLE_ADMIN 角色权限
- user 开头的请求需要有ROLE_USER 角色权限
- /system/monitor 需要有system_monitor权限
注意:这里配置hasRole 的时候不要写 ROLE_ 开头,不然会报错; 默认会处理加上默认前缀,可以通过修改
DefaultWebSecurityExpressionHandler上的defaultRolePrefix来自定义。
javaconfig 配置
固定方法
- hasRole() 有某个角色
- hasAnyRole() 有任何一个角色
- hasAuthority() 有某个权限
- hasAnyAuthority() 有任何权限
- hasIpAddress() 指定ip地址
表达式控制
spring Security使用Spring EL表达支持,可以更好的来控制权限;
示例:
1 | .antMatchers("/admin/**").access("hasRole('ADMIN')") |
通过access 方法中编写对应的表达式
| 表达 | 描述 |
|---|---|
hasRole([role]) | 如果当前主体具有指定角色,则返回true。默认情况下,如果提供的角色不以“ROLE_”开头,则会添加该角色。这可以通过修改DefaultWebSecurityExpressionHandler上的defaultRolePrefix来自定义。 |
hasAnyRole([role1,role2]) | 如果当前主体具有任何提供的角色(以逗号分隔的字符串列表给出),则返回true。默认情况下,如果提供的角色不以“ROLE_”开头,则会添加该角色。这可以通过修改DefaultWebSecurityExpressionHandler上的defaultRolePrefix来自定义。 |
hasAuthority([authority]) | 如果当前主体具有指定的权限,则返回true。 |
hasAnyAuthority([authority1,authority2]) | 如果当前主体具有任何提供的权限(以逗号分隔的字符串列表给出),则返回true |
principal | 允许直接访问代表当前用户的主体对象 |
authentication | 允许直接访问从SecurityContext获取的当前Authentication对象 |
permitAll | 始终评估为true |
denyAll | 始终评估为false |
isAnonymous() | 如果当前主体是匿名用户,则返回true |
isRememberMe() | 如果当前主体是remember-me用户,则返回true |
isAuthenticated() | 如果用户不是匿名用户,则返回true |
isFullyAuthenticated() | 如果用户不是匿名用户或记住我用户,则返回true |
hasPermission(Object target, Object permission) | 如果用户有权访问给定权限的提供目标,则返回true。例如,hasPermission(domainObject, 'read') |
hasPermission(Object targetId, String targetType, Object permission) | 如果用户有权访问给定权限的提供目标,则返回true。例如,hasPermission(1, 'com.example.domain.Message', 'read') |
表达式拓展
如果内置的表达式无法满足需求,那么可以拓展表达式,允许通过自定义的类应用到表达式;
首先声明一个要应用到表达式的bean
此bean中实现一个check 方法,做了一个校验的权限处理,如果请求参数中有auth 并且是true 就可以访问
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13@Component(value = "webSecurityCheck")
public class WebSecurityCheck {
public boolean check(Authentication authentication, HttpServletRequest request) {
String auth = request.getParameter("auth");
if("true".equalsIgnoreCase(auth)){
return true;
}
return false;
}
}应用到表达式中
注意前面需要加 @bean名称.方法名;
1
.antMatchers("/system/monitor").access("@webSecurityCheck.check(authentication,request)")
方法级别的控制
spring security 也支持注解的方式的控制权限;
开启方法控制
首先配置开启全局方法控制
1 | @EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true) |
方法控制注解
提供了4个注解来控制权限;
- @PreAuthorize 决定了是否可以访问实际调用的方法
- @PreFilter 在调用前执行参数的过滤
- @PostAuthorize 调用后检查权限(不常用)
- @PostFilter 调用后执行数据权限过滤
四个注解都是只有一个 value 值,支持编写表达式的方式来定义权限;
四个表达式中只有 @PreAuthorize 是常用的,其他的用的比较少;
@PreAuthorize
示例:
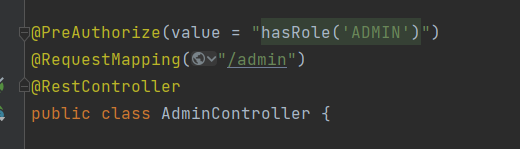
与参数配合获取权限
1 | @PreAuthorize(value = "#name != principal.username") |
可以结合方法上的参数来灵活的定制权限;
同时也可以结合 @P 注解 或spring data的@param注解使用方法参数别名
1 | @PreAuthorize("#c.name == authentication.name") |
@PreFilter
用于在方法执行前做集合数据过滤
此注解有2个属性,
value 是表达式
filterTarget 是当有多个参数的时候需要指定是哪个参数用在表达式
1 | /** |
示例: 定义一个有集合元素的方法,filterObject 表示集合中的遍历的一个属性,这里表示集合中的元素的值不等于read;
filterTarget 用于方法有多个参数的时候指定使用哪个参数集合;
1 | @PreFilter(value = "filterObject != 'read'",filterTarget = "data") |
@PostAuthorize
在方法执行完毕后做权限校验
@PostFilter
只有一个value值可设置,因为返回值只能一个;
1 | /** |
对获取到的结果做数据过滤操作;
示例:
1 | @PostFilter("hasPermission(filterObject, 'read') or hasPermission(filterObject, 'admin')") |


