Spring Security在内部维护一个过滤器链,其中每个过滤器都有特定的责任;
比如:
登录流程解析 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 登录认证流程解析认证的是通过一个对应的过滤器UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter
此类是一个过滤器继承 AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter
既然是过滤器首先看 doFilter 逻辑
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 private void doFilter(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException { if (!requiresAuthentication(request, response)) { chain.doFilter(request, response); return; } try { //核心代码获取 Authentication Authentication authenticationResult = attemptAuthentication(request, response); if (authenticationResult == null) { // return immediately as subclass has indicated that it hasn't completed return; } this.sessionStrategy.onAuthentication(authenticationResult, request, response); // Authentication success if (this.continueChainBeforeSuccessfulAuthentication) { chain.doFilter(request, response); } //验证成功后处理 successfulAuthentication(request, response, chain, authenticationResult); } catch (InternalAuthenticationServiceException failed) { this.logger.error("An internal error occurred while trying to authenticate the user.", failed); unsuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, failed); } catch (AuthenticationException ex) { // Authentication failed //认证失败后处理 unsuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, ex); } }
attemptAuthentication 是一个抽象方法,由 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 @Override public Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws AuthenticationException { if (this.postOnly && !request.getMethod().equals("POST")) { throw new AuthenticationServiceException("Authentication method not supported: " + request.getMethod()); } //获取用户名 其实就是request.getParam 获取 String username = obtainUsername(request); username = (username != null) ? username : ""; username = username.trim(); //获取密码 其实就是request.getParam 获取 String password = obtainPassword(request); password = (password != null) ? password : ""; //用户名和密码组装成 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authRequest = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(username, password); // Allow subclasses to set the "details" property setDetails(request, authRequest); return this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authRequest); }
this.getAuthenticationManager() 获取 权限管理器 AuthenticationManager
AuthenticationManager 这里的实现是 ProviderManager ,管理了多个 AuthenticationProvider 针对不同的认证方式有不同的实现,会根据开启了那些功能有多个实现;
执行 authenticate 方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 @Override public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException { Class<? extends Authentication> toTest = authentication.getClass(); AuthenticationException lastException = null; AuthenticationException parentException = null; Authentication result = null; Authentication parentResult = null; int currentPosition = 0; //有多个provider权限校验 int size = this.providers.size(); for (AuthenticationProvider provider : getProviders()) { //是否支持当前的校验 if (!provider.supports(toTest)) { continue; } if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace(LogMessage.format("Authenticating request with %s (%d/%d)", provider.getClass().getSimpleName(), ++currentPosition, size)); } try { //执行校验 这里看下 DaoAuthenticationProvider result = provider.authenticate(authentication); if (result != null) { copyDetails(authentication, result); break; } } catch (AccountStatusException | InternalAuthenticationServiceException ex) { prepareException(ex, authentication); // SEC-546: Avoid polling additional providers if auth failure is due to // invalid account status throw ex; } catch (AuthenticationException ex) { lastException = ex; } } 这里的代码省略。。。。。。 }
DaoAuthenticationProvider DaoAuthenticationProvider 使用 userdetailservice 查询dao的用户信息等;
调用 DaoAuthenticationProvider#authenticate
执行到 DaoAuthenticationProvider 的抽象父类 AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 @Override public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException { Assert.isInstanceOf(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken.class, authentication, () -> this.messages.getMessage("AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.onlySupports", "Only UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken is supported")); // authentication 就是之前封装的usernamepasswordtoken 从里面获取username String username = determineUsername(authentication); boolean cacheWasUsed = true; //这里用到了缓存 UserDetails user = this.userCache.getUserFromCache(username); if (user == null) { cacheWasUsed = false; try { //缓存中获取不到执行此逻辑 user = retrieveUser(username, (UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication); } catch (UsernameNotFoundException ex) { this.logger.debug("Failed to find user '" + username + "'"); if (!this.hideUserNotFoundExceptions) { throw ex; } throw new BadCredentialsException(this.messages .getMessage("AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.badCredentials", "Bad credentials")); } Assert.notNull(user, "retrieveUser returned null - a violation of the interface contract"); } try { //校验账户是否过期,索引等信息 this.preAuthenticationChecks.check(user); //进行密码比对的逻辑 additionalAuthenticationChecks(user, (UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication); } catch (AuthenticationException ex) { if (!cacheWasUsed) { throw ex; } // There was a problem, so try again after checking // we're using latest data (i.e. not from the cache) cacheWasUsed = false; user = retrieveUser(username, (UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication); this.preAuthenticationChecks.check(user); additionalAuthenticationChecks(user, (UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken) authentication); } this.postAuthenticationChecks.check(user); if (!cacheWasUsed) { //本地缓存添加 this.userCache.putUserInCache(user); } Object principalToReturn = user; if (this.forcePrincipalAsString) { principalToReturn = user.getUsername(); } //创建一个成功的 Authentication return createSuccessAuthentication(principalToReturn, authentication, user); }
本地缓存中获取不到后,执行此方法,开始获取我们配置的 UserDetailsService 调用我们定义的查询方法;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 @Override protected final UserDetails retrieveUser(String username, UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authentication) throws AuthenticationException { prepareTimingAttackProtection(); try { UserDetails loadedUser = this.getUserDetailsService().loadUserByUsername(username); if (loadedUser == null) { throw new InternalAuthenticationServiceException( "UserDetailsService returned null, which is an interface contract violation"); } return loadedUser; }
passwordEncoder 根据用户名查询到用户信息后调用 additionalAuthenticationChecks 执行密码匹配逻辑,会使用passwordEncoder 也就是一般需要我们配置的那个密码编码器
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 @Override @SuppressWarnings("deprecation") protected void additionalAuthenticationChecks(UserDetails userDetails, UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authentication) throws AuthenticationException { if (authentication.getCredentials() == null) { this.logger.debug("Failed to authenticate since no credentials provided"); throw new BadCredentialsException(this.messages .getMessage("AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.badCredentials", "Bad credentials")); } String presentedPassword = authentication.getCredentials().toString(); if (!this.passwordEncoder.matches(presentedPassword, userDetails.getPassword())) { this.logger.debug("Failed to authenticate since password does not match stored value"); throw new BadCredentialsException(this.messages .getMessage("AbstractUserDetailsAuthenticationProvider.badCredentials", "Bad credentials")); } }
//最后一步创建成功的认证,重新创建了 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken 并且可以通过 authoritiesMapper 再次从数据库中查询权限信息;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 protected Authentication createSuccessAuthentication(Object principal, Authentication authentication, UserDetails user) { // Ensure we return the original credentials the user supplied, // so subsequent attempts are successful even with encoded passwords. // Also ensure we return the original getDetails(), so that future // authentication events after cache expiry contain the details UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken result = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(principal, authentication.getCredentials(), this.authoritiesMapper.mapAuthorities(user.getAuthorities())); result.setDetails(authentication.getDetails()); this.logger.debug("Authenticated user"); return result; }
当认证成功后,调用 AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter#successfulAuthentication
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 protected void successfulAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain, Authentication authResult) throws IOException, ServletException { //将当前的认证信息放入 SecurityContextHolder 中 SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authResult); if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) { this.logger.debug(LogMessage.format("Set SecurityContextHolder to %s", authResult)); } //rememberMe 的相关逻辑 this.rememberMeServices.loginSuccess(request, response, authResult); if (this.eventPublisher != null) { this.eventPublisher.publishEvent(new InteractiveAuthenticationSuccessEvent(authResult, this.getClass())); } //可以 成功的处理器,可以自定义的,有时候会根据需求自定义 this.successHandler.onAuthenticationSuccess(request, response, authResult); }
同样失败后也会调用对应的方法 AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter#unsuccessfulAuthentication
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 protected void unsuccessfulAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationException failed) throws IOException, ServletException { //清空contextholder SecurityContextHolder.clearContext(); this.logger.trace("Failed to process authentication request", failed); this.logger.trace("Cleared SecurityContextHolder"); this.logger.trace("Handling authentication failure"); //清空rememberMe信息 this.rememberMeServices.loginFail(request, response); //失败的处理器,也是可以配置自定义的 this.failureHandler.onAuthenticationFailure(request, response, failed); }
总结下基本流程:
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 会拦截提交到loginurl 的请求 当前如果没有登录就从请求中获取用户名和密码 根据 用户名 调用自定义的userdetailservice 查询用户信息 查询到用户信息后校验用户的状态 并且使用passwordEncoder 进行密码比对 登录成功后将用户认证信息放入 SecurityContextHolder 中。同时执行登录成功的handler 登录失败后将用户认证信息 从 SecurityContextHolder 清空,同时执行登录失败的handler SecurityContextHolder 解析 SecurityContextHolder 是用来存储用户的认证的信息的,从中可以静态的获取认证信息;
可以获取到 SecurityContext
内部维护了一个 SecurityContextHolderStrategy 不同的实现;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 private static SecurityContextHolderStrategy strategy; private static int initializeCount = 0; static { initialize(); } private static void initialize() { if (!StringUtils.hasText(strategyName)) { // Set default strategyName = MODE_THREADLOCAL; } if (strategyName.equals(MODE_THREADLOCAL)) { strategy = new ThreadLocalSecurityContextHolderStrategy(); } else if (strategyName.equals(MODE_INHERITABLETHREADLOCAL)) { strategy = new InheritableThreadLocalSecurityContextHolderStrategy(); } else if (strategyName.equals(MODE_GLOBAL)) { strategy = new GlobalSecurityContextHolderStrategy(); } else { // Try to load a custom strategy try { Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(strategyName); Constructor<?> customStrategy = clazz.getConstructor(); strategy = (SecurityContextHolderStrategy) customStrategy.newInstance(); } catch (Exception ex) { ReflectionUtils.handleReflectionException(ex); } } initializeCount++; }
GlobalSecurityContextHolderStrategy 共享的认证信息;
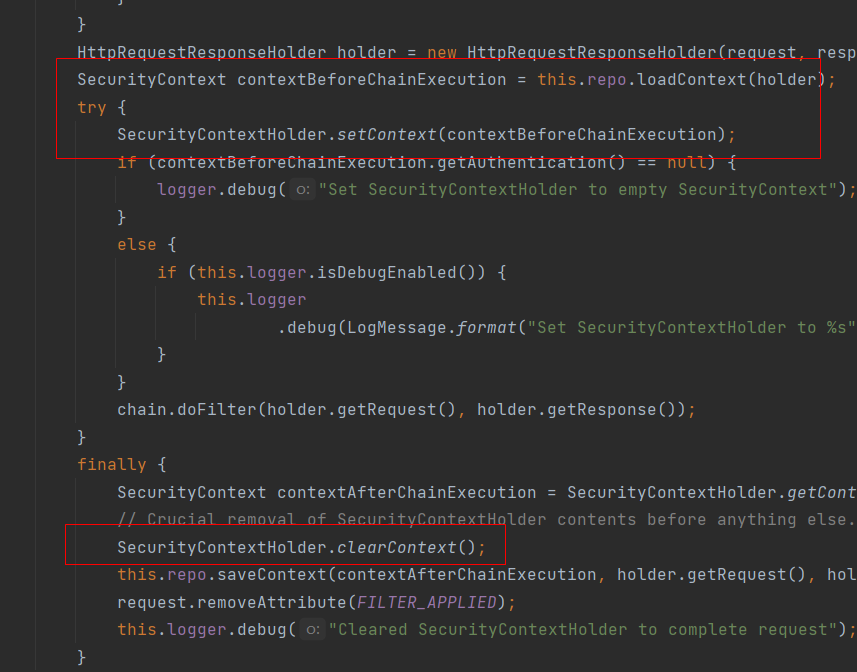
那么对于已经登录完成的用户下次请求是怎么放到 SecurityContextHolder 中的呢? 是通过一个过滤器 SecurityContextPersistenceFilter
SecurityContextPersistenceFilter 此过滤器的主要作用就是在请求前从 SecurityContextRepository 中 ,获取到认证信息放到 SecurityContextHolder 中,请求的最后同时将