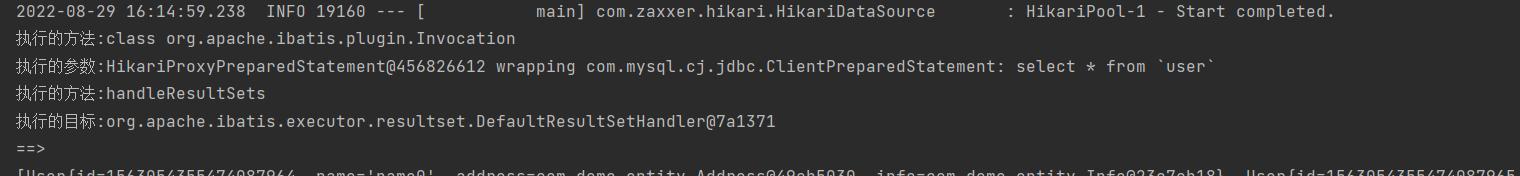
简单说明
在使用mybatis的时候非常常用的一个插件就是分页的插件。首先回顾下这个插件的使用。
- 引入对应的依赖
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| <dependency>
<groupId>com.github.pagehelper</groupId>
<artifactId>pagehelper</artifactId>
<version>5.1.2</version>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
|
- 声明并配置插件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| @Bean
public PageInterceptor pageInterceptor() {
PageInterceptor pageInterceptor = new PageInterceptor();
Properties properties = new Properties();
pageInterceptor.setProperties(properties);
return pageInterceptor;
}
List<Interceptor> interceptorList = new ArrayList<>();
interceptorList.add(pageInterceptor());
factoryBean.setPlugins(interceptorList.toArray(new Interceptor[interceptorList.size()]));
|
- 至此可以在普通的列表查询方法上做分页查询
1
2
3
4
5
6
| PageHelper.startPage(1, 10);
Page<User> page = (Page)userMapper.selectAll();
System.out.println(page.getPageSize());
page.getResult().forEach(x-> {
System.out.println(x);
});
|
插件原理

看下官网的说明,插件允许对一些执行方法做拦截。其实说白了就是能对框架内部的一些执行方法做增强。
可以修改输入结果 或输出结果,或做其他的事情。
能够执行操作的几个类是
- Executor 核心执行器类,基本的查询更新等相关调用方法
- ParameterHandler 参数处理器类
- ResultSetHandler 结果集处理类
- StatementHandler Statement 处理类
这几个都是比较核心的类.
而上面的分页插件既然是要执行分页应该是在查询结果的时候执行拦截把sql改写成分页的查询并包装返回结果。
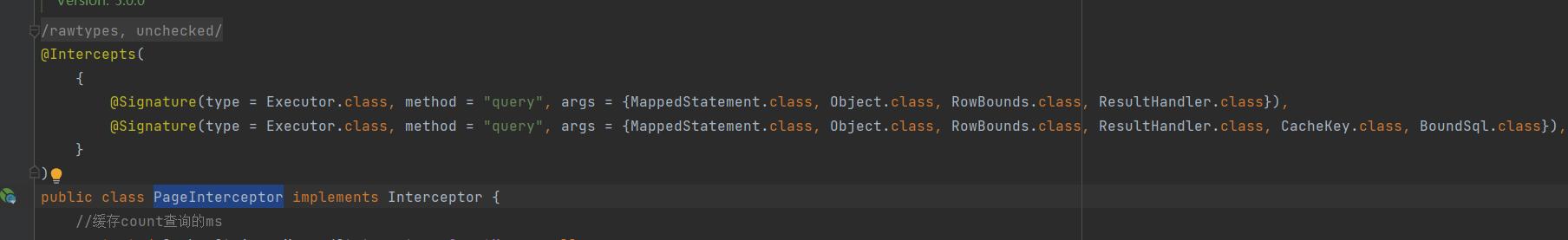
可以发现分页插件拦截的是 Executor 的query 方法。
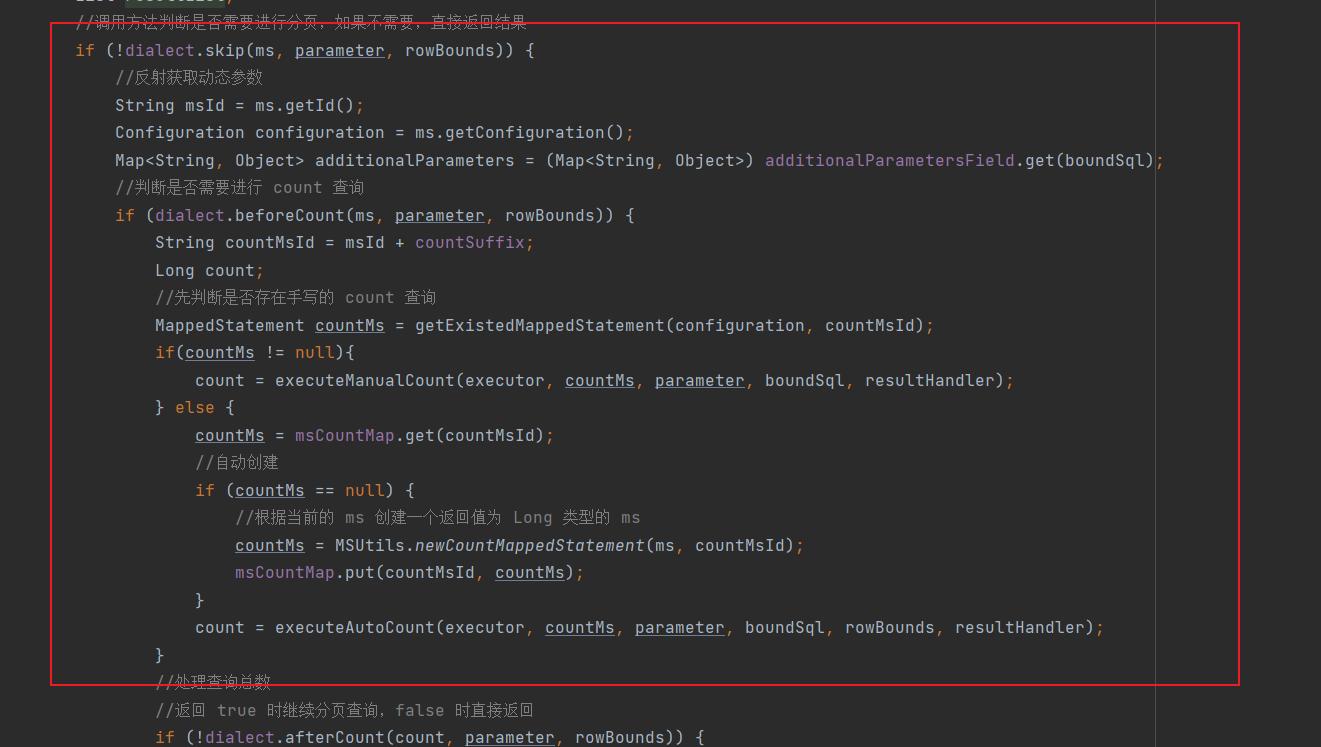
大体逻辑是拦截到对应的请求后。
判断当前的方法是否需要分页。
如果要分页,那么首先根据当前的查询sql 做一个count 查询操作,计算出分页的相关信息。
然后再查询指定页的列表查询结果。
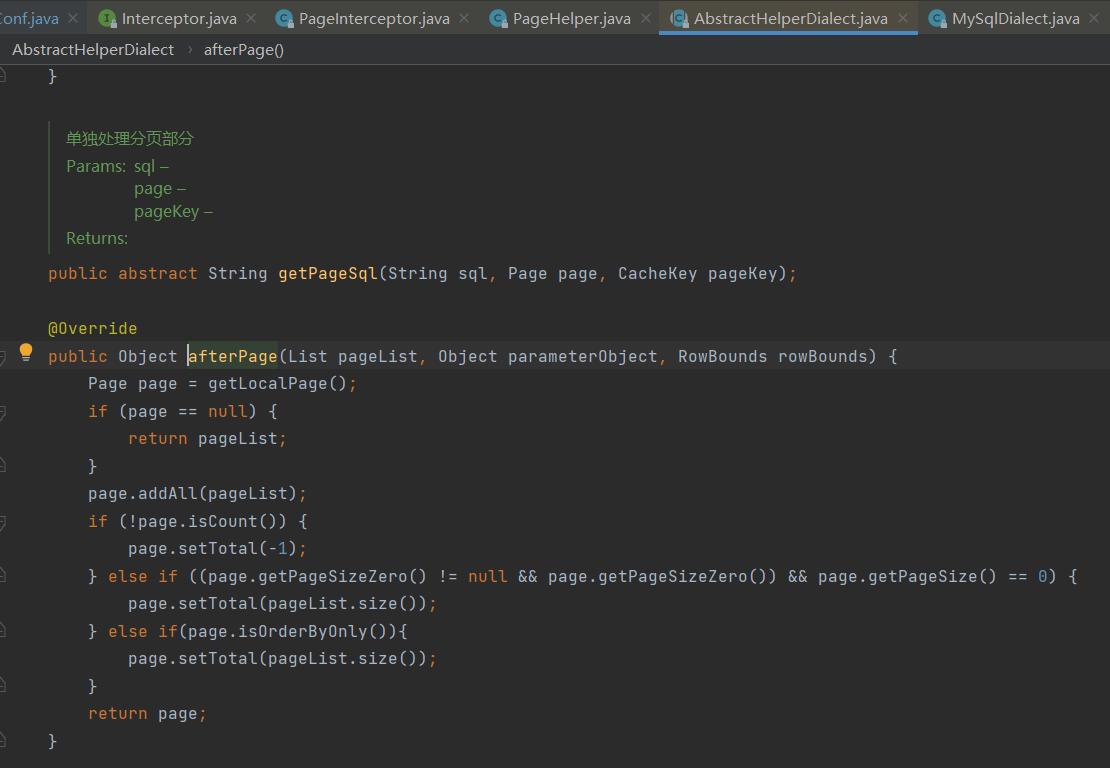
将最终的结果包装成一个包含分页信息的 Page对象,因为这个Page对象是实现了List的,所以可以和List 返回值兼容。
自定义插件
如果要实现一个自定义的mybatis 插件只需要简单的几步
- 定义 Interceptor 并实现 Interceptor
- @Intercepts 注解 声明要拦截的类和方法信息
- 将此自定义类交给 SqlSessionFactoryBean
假设要拦截 ResultSetHandler handleResultSets 方法对查询结果做一些处理。
定义插件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
|
@Intercepts(
{
@Signature(type = ResultSetHandler.class, method = "handleResultSets", args = {Statement.class}),
}
)
public class CustomResultInterceptor implements Interceptor {
@Override
public Object intercept(Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
Class<? extends Invocation> aClass = invocation.getClass();
Object[] args = invocation.getArgs();
Method method = invocation.getMethod();
Object target = invocation.getTarget();
System.out.println("执行的方法:"+aClass);
for (Object arg : args) {
System.out.println("执行的参数:"+arg);
}
System.out.println("执行的方法:"+method.getName());
System.out.println("执行的目标:"+target);
System.out.println("==>");
Object proceed = invocation.proceed();
return proceed;
}
@Override
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
}
@Override
public Object plugin(Object target) {
return Plugin.wrap(target, this);
}
}
|
配置到SqlSessionFactoryBean
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
|
@MapperScan(basePackages = "com.demo.mapper")
@Configuration
public class MyBatisConf {
@Bean
public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory(DataSource dataSource) throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactoryBean factoryBean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
factoryBean.setDataSource(dataSource);
PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver pathMatchingResourcePatternResolver = new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver();
Resource[] resources = pathMatchingResourcePatternResolver.getResources("classpath:mappers/com/demo/mapper/*.xml");
factoryBean.setMapperLocations(resources);
factoryBean.setTypeHandlersPackage("com.demo.conf.type_handlers");
List<Interceptor> interceptorList = new ArrayList<>();
interceptorList.add(pageInterceptor());
interceptorList.add(optionalResultInterceptor());
factoryBean.setPlugins(interceptorList.toArray(new Interceptor[interceptorList.size()]));
return factoryBean.getObject();
}
@Bean
public PageInterceptor pageInterceptor() {
PageInterceptor pageInterceptor = new PageInterceptor();
Properties properties = new Properties();
pageInterceptor.setProperties(properties);
return pageInterceptor;
}
@Bean
public CustomResultInterceptor optionalResultInterceptor() {
CustomResultInterceptor customResultInterceptor = new CustomResultInterceptor();
return customResultInterceptor;
}
}
|
执行查询方法查看打印结果